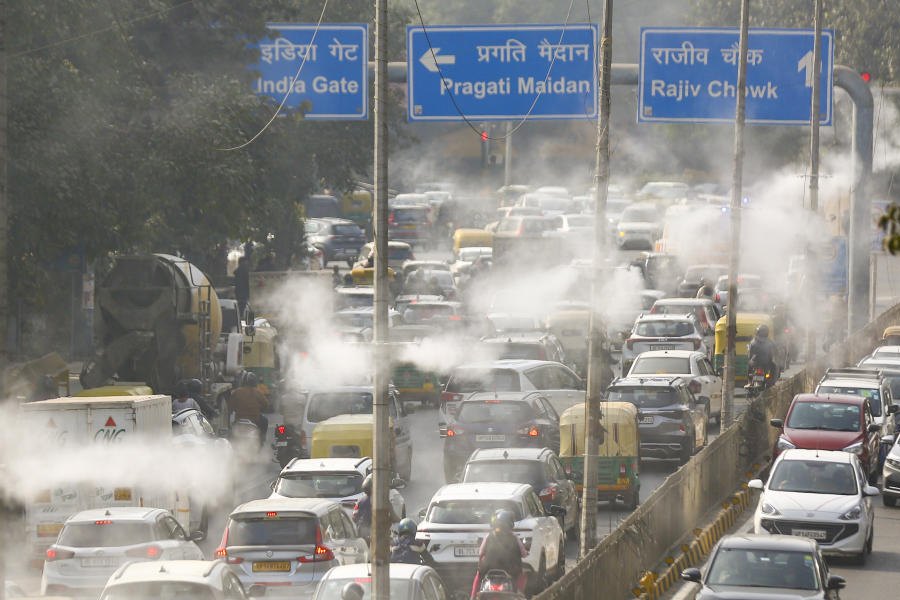
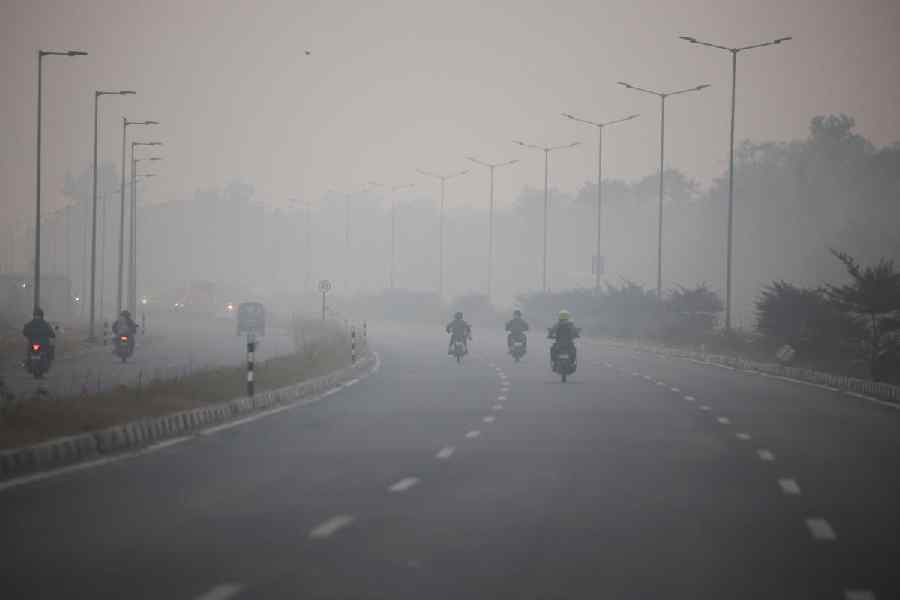
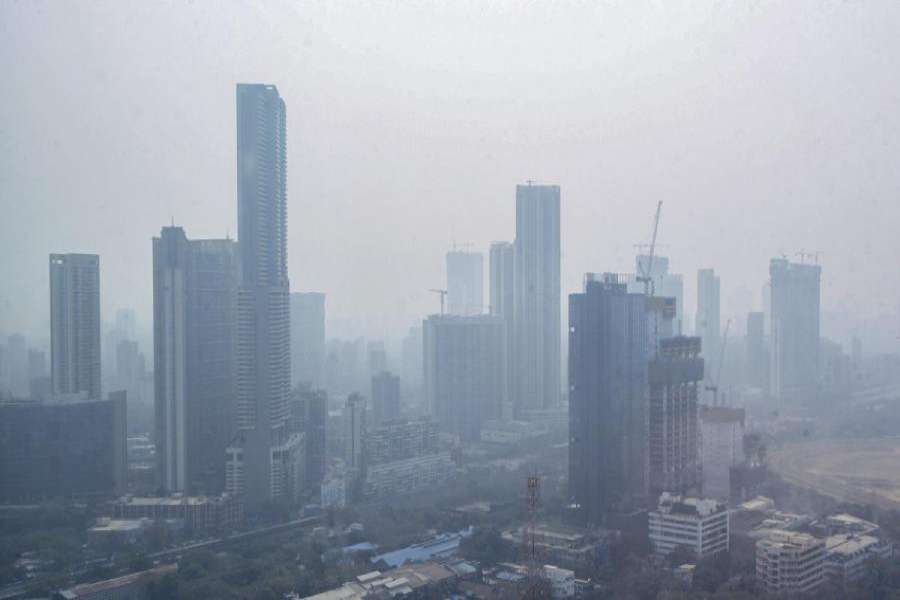
The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) invoked stricter curbs under Stage-III of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) across Delhi-NCR as pollution levels spiked sharply on Saturday, citing unfavourable weather conditions and poor dispersion of pollutants.
The national capital’s 24-hour average air quality index (AQI) stood at 349, but worsened rapidly through the morning, touching 401 by 10 am.
The sudden deterioration, the CAQM said, was “owing to slow wind speed, stable atmosphere, unfavourable weather parameters and meteorological conditions and lack of dispersal of pollutants”.
In view of the rising pollution trend, the CAQM GRAP Sub-Committee decided to enforce all measures under Stage-III of GRAP, categorised as ‘Severe’ air quality, with immediate effect across the National Capital Region.
These measures will operate alongside restrictions already in place under Stages I and II. Under Stage-III, non-essential construction and demolition activities stand suspended. Stone crushing and mining operations are also barred.
The restrictions extend to vehicular movement, with BS III petrol and BS IV diesel four-wheelers prohibited in Delhi, Gurugram, Faridabad, Ghaziabad and Gautam Buddh Nagar.
The curbs also include a ban on older diesel goods vehicles entering Delhi. Schools up to Class 5 will shift to hybrid mode, while offices across Delhi-NCR may function with only 50 per cent staff on-site.
GRAP is a seasonal pollution-control framework implemented in Delhi-NCR during winter months, when air quality routinely deteriorates.
It is structured in four stages based on AQI levels — Stage I (Poor, AQI 201–300), Stage II (Very Poor, AQI 301–400), Stage III (Severe, AQI 401–450), and Stage IV (Severe Plus, AQI above 450).