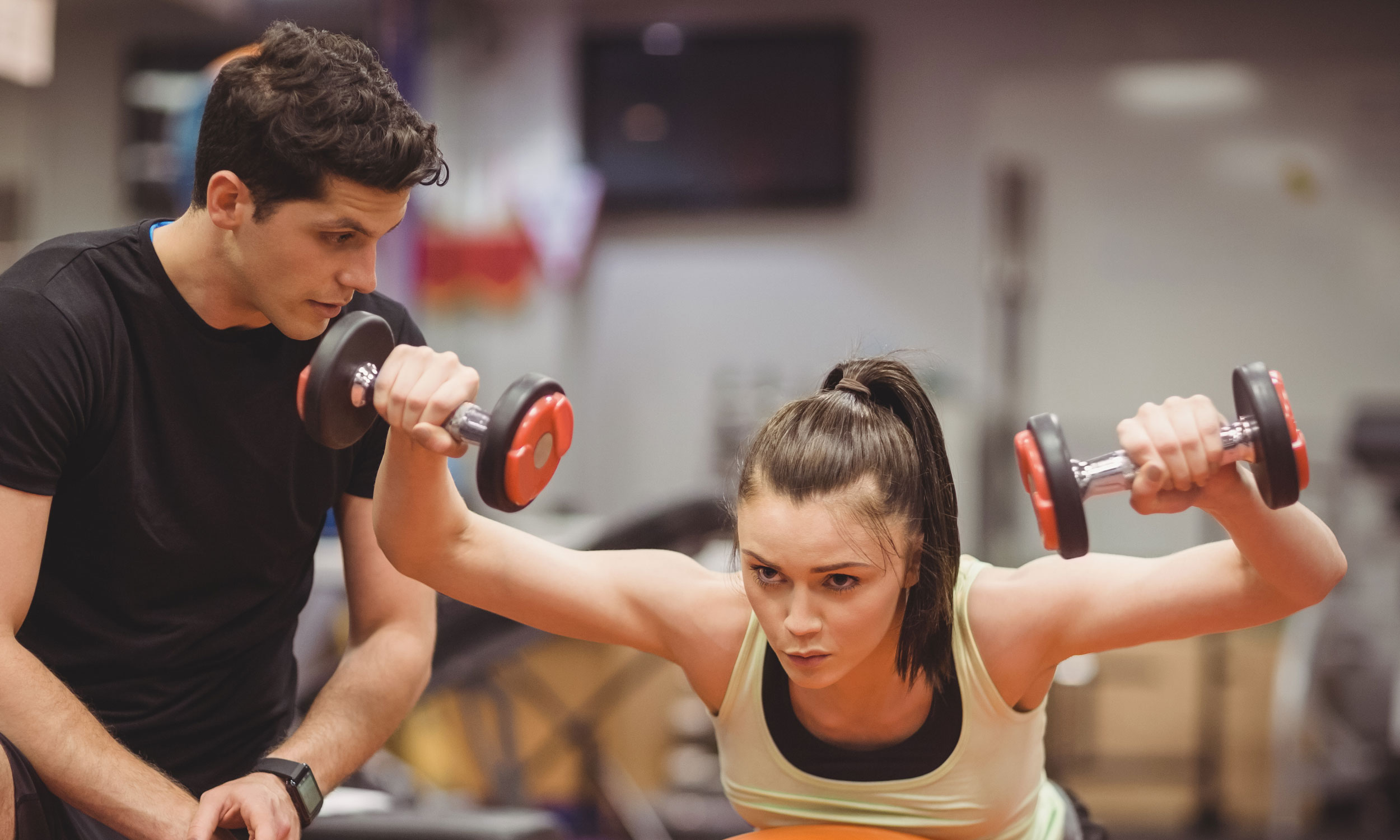
The term weight training brings up visions of sweaty young men dedicating hours to replicating a body like that of Arnold Schwarzenegger. But sustained weight and strength training not only has myriad hidden benefits but will also not make you bulky.
Many older adults are satisfied with their 30-minute daily walk. Although it is better than nothing, it will not help prevent falls or retain independence with increasing age. And the ability to take care of yourself has become increasingly important now, when adult children no longer live with ageing parents.
With age and little use, muscles waste away. Frailty, loss of balance and further fractures and injury can occur. Mortality unnecessarily increases. Falls are faster and more severe in women with their smaller body mass. Almost 20 per cent of the Indian population is now older than 60, and the annual incidence of hip fractures is around 6,00,000. Based on current mortality data, an estimated 40 per cent of these individuals die within a year.
To prevent this, everyone needs to train with weights. The recommended units are 1-2 kilos in women and 3-5 kilos in men. About 20-30 repetitions should be done at least every alternate day. The exercises will help develop both muscle mass and bone strength. As a result, balance improves and falls become less likely. As the muscle fibres increase in number and size, they utilise glucose more effectively, which results in better diabetic control. Weight training metabolises fat so body weight too reduces.
Weight training can be learnt in the gym, with a physiotherapist or by watching videos. Start with just 10 repetitions and then increase the number with 20-second rest intervals. Spend around 30 minutes on weight training three to four times a week.
Walking, jogging and running are excellent for cardiovascular fitness. A slow ambulatory stroll is really not that helpful. If you can converse with your walking partner, you need to walk faster. You should be able to cover a distance of 4km in 40 minutes. Cycling is also a good aerobic activity. Unfortunately, the wheels do a great deal of the work, so you need to cover 10 kilometres for an effective workout. An exercise cycle is as effective as the traditional cycle. Swimming is an excellent low impact workout, which keeps the weight off the joints. This means it can be done by people with injuries and arthritis. You need to put in at least 30 minutes of swimming. This means spending around 40 minutes in the pool to allow for rests between laps.
Exercise causes the muscles to contract. It is important to stretch them after exercise to bring them back to their pliable resting state. It also reduces the aches and pain that may follow exercise. Stretches can be learnt in a gym, as part of a yoga class or by watching YouTube.
As we age, it becomes increasingly important to exercise. The body has to be maintained with regular structured activity (not housework). Remember that in the case of muscles, if you don’t “use it, you will lose it”.