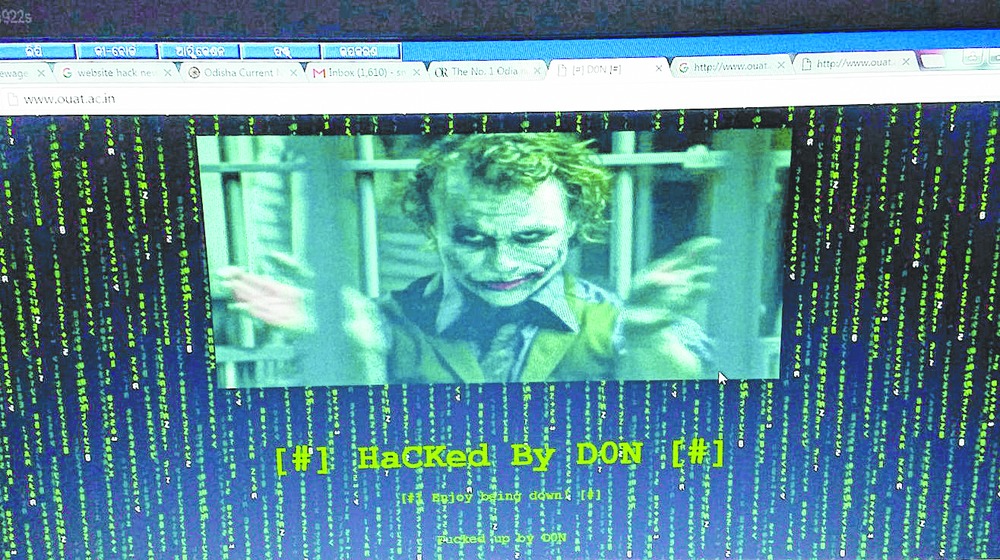
Bhubaneswar, Jan. 19: Last night, a private engineering college student reached Khandagiri police station and confessed that he hacked the official website of the Odisha University of Agriculture and Technology (OUAT).
The www.ouat.ac.in website, had been hacked on January 15, following which the university deactivated the server.
After interrogation, the police came to the conclusion that the intention of the student was not to cause any damage or data theft but merely thrill.
The Telegraph spoke to professional ethical hacker N. Vijay Kumar on what hacking is all about.
♦ What is hacking?
In the 80's, the term "hacker" was used for someone who experimented with different things constructively. The term has now come to mean a person who breaks into computers for stealing, changing or destroying information.
♦ Is hacking a part of the computer engineering curriculum?
A bachelor's degree programme in computer science and engineering covers many subjects that can be used as the foundation for hacking. A sound knowledge about how computers work and behave in different scenarios are important to perform hacking. These are obviously a part of the curriculum.
♦ Is it possible for average computer engineering students to hack websites without any training?
There are extremely low chances of that.
♦ Where do people learn hacking? Are there institutes offering such courses? How much do they charge?
Hacking is experimenting with computers to identify the vulnerability. Vulnerabilities are weak points in a program that are the result of poor coding. When you know a computer well, you can predict it's behaviour and take advantage of vulnerabilities to break into the servers. There are many institutes in Odisha that teach how hacking is done and how to protect ourselves against it. We even have globally-accepted online courses that offer certification to ethical hackers, namely, Certified Ethical Hacker or the CEH. These courses cost between Rs 30,000 and Rs 50,000 and are of six months' duration.
♦ Does it have a job market?
There is a huge demand for ethical hackers. Every year, around 77,000 ethical hackers are required in government and public sectors and only 35,000 of them are qualified. The main objective of such recruits is to test applications for vulnerability and apply patches on them before any malicious hacker takes an advantage.
♦ How can an average student practise hacking without landing in trouble?
Different applications are built for practising hackers. We have Damn Vulnerable Web Application, Mutillidae and websites such as HackThisSite.org. To practise hacking into computers, we have Metasploitable and bunch of other applications.
♦ How websites can be protected from being hacked?
Vulnerabilities in websites are mostly due to improper handling of user input data. Hackers can only break into computers when there is vulnerability. Thus, developers must check for the vulnerabilities and keep themselves updated with new industry standards and best practices. Since, there is no such thing as perfect, it is impossible to build an application which is 100 per cent secure.