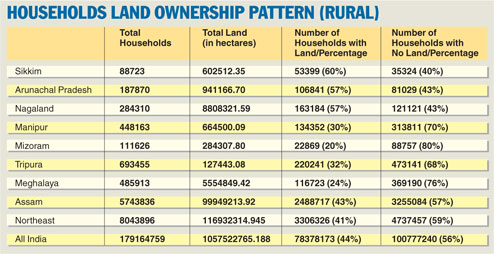
Shillong/Guwahati, July 3: Surpassing the national average, nearly 60 per cent of rural households in the Northeast have no land while manual casual labour is the main source of income, provisional data from the Socio- Economic and Caste Census (SECC), 2011 for rural India has revealed.
The data, released in New Delhi today, revealed that of the 80,43,896 households located in rural Northeast in eight states, only 33,06,326 (41 per cent) have land while 47,37,457 (59 per cent) households are landless.
Across rural India, there are 7,83,78,173 (44 per cent) households with land, and 10,07,77,240 (56 per cent) households with no land.
The total land in rural Northeast has been pegged at 11,69,32,314.945 hectares against the national figure of 1,05,75,22,765.188 hectares.
Among the northeastern states, Sikkim has the highest number of households with land. From the total rural households of 88,723, there are 53,399 or 60 per cent households with land.
The state with the least number of households with land is Mizoram, followed by Meghalaya. Most of the land in Meghalaya is privately owned. Of the 4,85,913 households, there are only 1,16,723 (24 per cent) households with land.
Moreover, the data revealed, the main source of income of the rural households in the Northeast is manual casual labour, with 39.03 per cent engaged in it. The next source of income is cultivation with 33.04 per cent of the households engaged in it.
Across rural India, 30.1 per cent of the households depend on cultivation as the main source of income while 51.14 per cent are into manual casual labour.
While 0.37 per cent of the rural households across India depend on begging/charity/alms collection as the main source of income, the percentage in the Northeast for the same is 0.56 per cent, the data revealed.
Combining both the rural and urban areas, the Northeast has 94,04,103 households (80,43,896 rural and 13,60,207 urban). There are 45,173 villages against 224 towns.
The provisional socio-economic data for rural India was completed in all the 640 districts. The data will be used in evidence-based planning for rural development and poverty reduction needs to be undertaken immediately.
In an official communiqué, the Union rural development ministry has decided to use the SECC data in all its programmes.
The programmes include housing for all, education and skills thrust, MGNREGA, National Food Security Act, interventions for the differently-abled, interventions for women-led households, and targeting of households/individual entitlements on evidence of deprivation, and others.
Assam illiteracy
The Socio Economic and Caste Census, 2011 says there is over 30 per cent illiteracy in Assam, which has a population of 2,84,51,916.
The report found that 91,21,670 people in Assam could not read and write, which is the third highest number of illiterates after Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya in the Northeast.
The illiteracy figure in Arunachal Pradesh is 39.31 per cent, in Meghalaya 33.4 per cent, in Nagaland 29.73 per cent, in Manipur 26.36 per cent, in Mizoram 25.3 per cent and in Tripura 22.09 per cent.
Among the literates in Assam, only 2.21 per cent is either graduate or higher secondary (Plus II) pass.
In the field of employment and income, 12.27 per cent of the total households in Assam has salaried jobs. The total number of households in the state as per the census is 57,43,836.
Among the salaried households, 7.61 per cent is engaged in the government sector followed by 3.8 and 0.88 per cent in private and public sectors respectively.
There are 76.89 per cent households in Assam where the monthly income of the highest earner is less than Rs 5,000. While 14.53 per cent similar households have monthly income between Rs 5,000 and Rs 10,000, 8.58 per cent such households earn Rs 10,000 or more.
The census has found that manual casual labour is the main source of income for 42.50 per cent households in the state. Cultivation is the second main source of income with 29.18 per cent households opting for it. Over five per cent households are engaged in part time or full time domestic service. Rag-picking is a source of income for 0.21 per cent households.
In terms of assets ownership, the census has found that 63.66 per cent households have mobile phones, motorised two, three and four-wheelers for 12.35 households and refrigerator for 5.31 per cent households.
According to the census, 4,08,746 households out of 57,43,836 in Assam pay income tax or professional tax to the government.
Among the total households in the state, 8.7 per cent households comprise Scheduled Castes, 14.28 per cent Scheduled Tribes, 35.52 per cent from other castes and tribes and 41.49 per cent fall under the "others" category.